mash
 I’m pleased to announce the release of a web based version of BeerSmith 3 along with a desktop BeerSmith 3.2 update. The web based version allows you to edit your cloud based recipes from anywhere by simply logging into your cloud account at BeerSmithRecipes.com. BeerSmith Web Highlights Web based recipe editing from any browser by […]
I’m pleased to announce the release of a web based version of BeerSmith 3 along with a desktop BeerSmith 3.2 update. The web based version allows you to edit your cloud based recipes from anywhere by simply logging into your cloud account at BeerSmithRecipes.com. BeerSmith Web Highlights Web based recipe editing from any browser by […]  This week I wanted to share a more detailed look at the upcoming Web based version of BeerSmith which is scheduled for release in June of 2021. It will be available to all Gold+ license holders of BeerSmith 3. When released, you can simply log into your existing BeerSmithRecipes.com account and edit recipes in your […]
This week I wanted to share a more detailed look at the upcoming Web based version of BeerSmith which is scheduled for release in June of 2021. It will be available to all Gold+ license holders of BeerSmith 3. When released, you can simply log into your existing BeerSmithRecipes.com account and edit recipes in your […] Brewery plans to build production facility and restaurant on rural land north of Sydney.
The post WA’s Beerfarm confirms major NSW expansion plans appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 This week I take a look at one of Germany’s most popular beer styles, the light lager known as German Helles. Helles is a traditional German Lager produced primarily in Southern Germany (Bavaria) around Munich. The word “hell” in German can be roughly translated as “pale, light or bright” in English. The History of Helles […]
This week I take a look at one of Germany’s most popular beer styles, the light lager known as German Helles. Helles is a traditional German Lager produced primarily in Southern Germany (Bavaria) around Munich. The word “hell” in German can be roughly translated as “pale, light or bright” in English. The History of Helles […] Bright revamp their Mash Club – one of the country’s oldest subscription models.
The post Beer club helps brewery look on the Bright side appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 Dr Charlie Bamforth joins me this week to discuss foam and head retention in beer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in This Week’s […]
Dr Charlie Bamforth joins me this week to discuss foam and head retention in beer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in This Week’s […] Feral’s new Shooter’s Juicy IPA is shaping up as their biggest limited release ever.
The post Feral Brewing’s Shooter’s Juicy IPA is here! appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 John Blichmann joins me this week to discuss ways to simplify your brew day with “common sense brewing”, beer brewing and intelligent use of your equipment. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your […]
John Blichmann joins me this week to discuss ways to simplify your brew day with “common sense brewing”, beer brewing and intelligent use of your equipment. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your […]  Mitch Steele joins me this week to discuss brewing low-calorie and low carbohydrate beer as well as seltzer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […]
Mitch Steele joins me this week to discuss brewing low-calorie and low carbohydrate beer as well as seltzer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […]  Chris Graham from MoreBeer joins me this week to discuss All-in-one brewing equipment options for home brewers. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]
Chris Graham from MoreBeer joins me this week to discuss All-in-one brewing equipment options for home brewers. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […] San Diego, CA (October 22, 2020) – PourMyBeer partners with Tappizza, San Diego’s latest pizza destination, to provide the ultimate pizza and beer experience with a 21-tap self-serve beer and hard seltzer beverage wall. Tappizza, located at 8242 Mira Mesa Blvd, is elevating the dining experience by putting its customers in control of their drinks, […]
The post San Diego Now Home to a Pizza and PourMyBeer Haven appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
 Gordon Strong joins me for a discussion on German Lager beer styles and some tips for making the perfect lager. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio […]
Gordon Strong joins me for a discussion on German Lager beer styles and some tips for making the perfect lager. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio […]  This week I take a look at methods for doing sensory analysis of hops as well as some of the resources available to understand hop flavor and aroma better. Understanding Hop Flavor and Aroma For a few years now I’ve been doing presentations on beer recipe design where I encourage brewers to get more familiar […]
This week I take a look at methods for doing sensory analysis of hops as well as some of the resources available to understand hop flavor and aroma better. Understanding Hop Flavor and Aroma For a few years now I’ve been doing presentations on beer recipe design where I encourage brewers to get more familiar […]  I’m happy to announce the BeerSmith Mobile 3.1.9 update has been released for Android, iPhone/IOS and the Amazon app store. The app is being released on an “rolling” basis to existing users or via the app store over the next week. More Value, Costs Less The new BeerSmith Mobile release is a significant improvement over […]
I’m happy to announce the BeerSmith Mobile 3.1.9 update has been released for Android, iPhone/IOS and the Amazon app store. The app is being released on an “rolling” basis to existing users or via the app store over the next week. More Value, Costs Less The new BeerSmith Mobile release is a significant improvement over […]  Jamil Zainasheff from Heretic Brewing joins me this week for a beer brewing question and answer session. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]
Jamil Zainasheff from Heretic Brewing joins me this week for a beer brewing question and answer session. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]  Andreas Krennmair joins me this week to discuss his new book on the history of Vienna Lagers. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]
Andreas Krennmair joins me this week to discuss his new book on the history of Vienna Lagers. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]  This week Marshall Schott joins me to discuss how many “short and shoddy” shortcuts you can take when brewing beer and still produce good beer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser […]
This week Marshall Schott joins me to discuss how many “short and shoddy” shortcuts you can take when brewing beer and still produce good beer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser […]  I’m happy to announce the official release of the BeerSmith 3.1 update. This update includes some significant updates to the BeerSmith data storage model, TILT data import, new brewing features and a large number of bug fixes. This release is also a very important foundational step towards establishing both an online version of BeerSmith and […]
I’m happy to announce the official release of the BeerSmith 3.1 update. This update includes some significant updates to the BeerSmith data storage model, TILT data import, new brewing features and a large number of bug fixes. This release is also a very important foundational step towards establishing both an online version of BeerSmith and […]  Buy BeerSmith 3 Download BeerSmith 3 Here is a summary of the new features coming in the BeerSmith 3.1 desktop update. I have posted the open beta version on the main download page at BeerSmith.com, and plan to publish the formal release in the next week or two. You can find additional details for all […]
Buy BeerSmith 3 Download BeerSmith 3 Here is a summary of the new features coming in the BeerSmith 3.1 desktop update. I have posted the open beta version on the main download page at BeerSmith.com, and plan to publish the formal release in the next week or two. You can find additional details for all […] 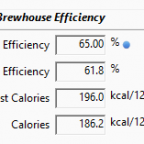 This week I take a look at how you can use BeerSmith brewing software to adjust the brewhouse efficiency for your individual equipment setup. Understanding Brewhouse Efficiency Brewhouse efficiency is simply a measure of how efficient your all grain brewing system is at converting pounds (or kilograms) of grains into Original Gravity (OG) points going […]
This week I take a look at how you can use BeerSmith brewing software to adjust the brewhouse efficiency for your individual equipment setup. Understanding Brewhouse Efficiency Brewhouse efficiency is simply a measure of how efficient your all grain brewing system is at converting pounds (or kilograms) of grains into Original Gravity (OG) points going […] Forgeworks 10 bbl Brewhouse - $71,306
The Good: Reasonable price, solid build quality, gets the wort production job done.
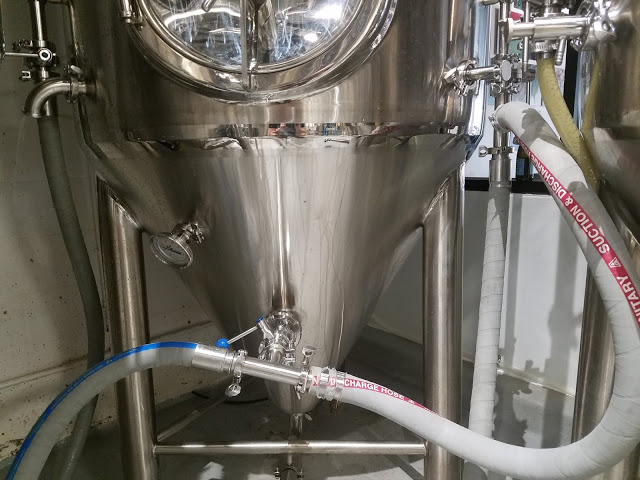
The Bad: A few design head-scratchers on the mash tun. It has a huge volume below the false bottom (~90 gallons/3 bbl). The under-screen spray balls spray directly into the supports making them useless (the connection for them is also around back making it difficult to access). The torsion ring on the rakes wasn't adequately tightened when we received it causing the rakes fell off mid-mash a few batches in. No issues since properly tightening. Originally the pickup arm in the kettle extended into the center (right into the trub cone), but they swapped us our for a shorter one that is now standard.
Verdict: Satisfied with it so far, but not thrilled given things like having to pull the false bottom to clean underneath/between after the last brew of the week (the plates can be annoying to remove, but not bad compared to some other systems).
MidCo EC300 Burner - $1,070
The Good: Plenty of heat to have the kettle close to a boil by the time run-off is finished.
The Bad: The burner's control board is incredibly sensitive to moisture, just a few drops and it is fried. A fact that it would have been nice to have a warning about from Forgeworks (they said some breweries have had it happen multiple times). Otherwise it has just been a learning curve to wait longer to turn it on and throttle the gas to avoid boil-overs. Our beers are 1-2 SRM darker than predicted thanks to direct fire, but not really the burner's fault.
Verdict: Steam would have been great, but wasn't in our budget. We haven't had issues since covering the control board with a plastic baggie (we've got a spare controller too). We were told that MidCo had a waterproof housing almost complete last fall, but haven't heard an update since.
Thermaline Heat Exchanger - $4,198.72
The Good: Their website allow you to input the parameters (volume, desired chilling rate, ground water/glycol temperature) and they build a unit to accommodate. That seemed to work for us as the chill times seem to line up reasonably.
The Bad: Nothing major to complain about. In the summer we do have to slow run-off as the second stage (glycol) doesn't lower the temperature compared to ground water by more than a degree or two at full blast.
Verdict: Might have been worth it to go a bit more over-sized, but no issues with the build-quality, durability etc.
Apex 10/20 bbl Fermenters - $7,500/10,700
The Good: The price is reasonable. We've got the "new style" 10 bbls that have an easy-rotate racking. The 2 inch dumps at the bottom rarely get clogged with hops, and the 4 inch dry hop ports work well, especially with our hop doser (below).
The Bad: The 20 bbl tank is the "old style" meaning the racking arm is just a tri-clamp. Not ideal, but it works fine especially after switching to a Teflon gasket. The big issue on that tank is with the hop port, the literature said it was a 6 inch, but it turned out to be a DIN150 (European fitting). Apex had been aware of this for 6 months and it took me ordering a gasket (to confirm the size), a custom reducer, and a new clamp all from Sanitary Fittings to resolve the issue.
There is a minor issue with one of the 10 bbl fermenters as well, the sparyball arm is just a little short which makes reassembly a two person operation (one to push, one to clamp).
Verdict: Given the issues and poor service with the 20 bbl, I'm hesitant to order more tanks from them when the time for expansion comes. Especially as they don't manufacture the tanks, the only advantage of going with them rather than directly from a Chinese manufacturer would be service.
Colorado Brewing Double Keg Washer - $6,370
The Good: Great price for an semi-automated keg washer. It rinses, washes, sanitizes, and purges two kegs at a time without intervention. As long as everything is connected and the reservoirs are filled, we rarely have an issue (other than hops in the occasional keg plugging up). The cycles are customizable, so we've tweaked them. We run a double cycle on our sour kegs, and no issues so far sharing them with clean beers.
The Bad: It's been a bit of a chore to deal with the issues that have arisen in one year of use: casters fell off, weld on one of the pots failed, software "disappeared", gas solenoid failed etc.
Verdict: The company has been great at dealing with these issues as they've occurred, shipping us replacement parts, paying for a welder etc. That said, I'd rather have not spent so much time dealing with it.
Marks Mini-Hop Doser - $495
The Good: Allows us to add hops with minimal oxygen pick-up. Safer than dry hopping loose (no risk of foam-up). Ability to add hops to a tank without venting the head pressure.
The Bad: Nothing big, although expect to double the cost of the unit itself in fittings. We have 4 inch butterfly valves on our tanks and move the doser between them as needed.
Verdict: Not sure what we'd do without it... oh I do because we we're able to use it on our 20 bbl because of the wonky port size (run CO2 and hope you don't get a face full of beer).
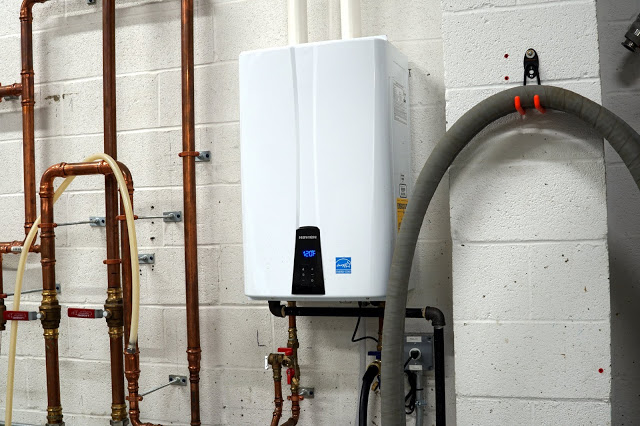
Navien Tankless Water Heater Standard Model - $1,260
The Good: Outputs up to 180F, plenty hot for collecting water for the mash and sparge or pasteurizing a line. Relatively inexpensive to buy and operate compared to a traditional always-on HLT.
The Bad: In the winter 180F output runs at 3 gallons/min. Helps to have a tank with an electric element to speed things up, or pre-collect water the night before.
Verdict: At our scale, and without steam this made the most sense and we're still happy with it. Two units can be daisy-chained together if we want to speed things up (e.g., first heats to 140F, second to 180F).
The Good: It's considerably less expensive than even a used propane-powered forklift. It's good in tight spaces because it's human powered, and powerful enough to lift a rack with two barrels. Being electric, it doesn't produce fumes that could negatively effect barrel-aging beers.
The Bad: Given the legs in front, it can't get around larger pallets, or standard pallets the long way. It is propelled by pushing, and weights over 1,200 lbs (plus whatever you are moving up to 2,200 lbs more). Only one wheel turns with steering making direction changes difficult. It also needs additional height above it, which can be tricky in a building with HVAC, lights, doorways etc.
Verdict: With our relatively cramped space, a forklift doesn't make sense, this gets the job done.
FlexTanks - $460-$1,190
The Good: They are inexpensive compared to stainless steel totes, while being easier to use than IBCs (international bulk containers). They have standard 1.5" tri-clamp fittings and sample ports. We mainly use the 300 gallon ones to hold bulk sour beer waiting for barrels, or to dilute barrel-aged beer that is too oaky (especially with so many first-use barrels). The 80 gallon FlexTanks are for fruit additions, where the large opening makes them easier to fill and empty than a barrel.
The Bad: They can only take ~1 PSI, so most of the movement has to be from gravity. The gasket on the lids is round and doesn't have a grove to sit in. This makes it is difficult to align without dropping in.
Verdict: They were a good place to start thanks to the price, but stainless would be more versatile and foolproof if you have the money.
EuroTransport Container Dimple Jacketed - $6,595
The Good: It's a movable, stainless-steel, temperature-controlled tank. We use it as our blending tank for sour barrel-aged beers. The bottom port is for liquid in/out (with a T for the sample port), and the two side ports for the temperature probe and carbonation stone. We currently have it off the pad, so it is nice to be able to pallet-jack it onto the pad for cleaning.
The Bad: It's odd that a jacketed tank doesn't have a built-in thermowell for the temperature probe. We use corny fittings for some kegs anyway, but it is weird to have a tank like this with a gas poppet on top. While the tank is jacketed, it isn't double walled so it sweats like crazy in the summer, we need to insulate it.
Verdict: Reasonably happy with it, but it requires a bit of a unique situation (like ours) to justify this over a standard brite tank.
XpressFill XF4500 - $6,295
The Good: It's a reasonable price for a four-head counter-pressure bottle filler. Does four bottles a minute when everything is humming along.
The Bad: We had some issues early on with the fill sensor. One or two heads would indicate that the bottle was filled even when it was empty. Turned out it was a drop of condensation on the CO2 line "falsely" completing the circuit. Not a problem now that we know what to do. One of the switches won't stay in the off position, which can cause the pneumatic foot to rise unexpectedly.
Verdict: I'm happy with it. Worth the added cost over a gravity filler for us because it reduces oxygen exposure, and allows us to bottle partially (or fully) carbonated beer. Our general approach is to chill the beer in the blending tank, prime with sugar and rehydrated yeast, agitate the tank, then pump in CO2 through the stone to get to ~1.5 volumes of CO2. The yeast does its job to bring the carbonation to target in the bottle, and we don't have to worry about predicting residual CO2 in barrels stored in ambient conditions.
Update: We had to cut down the stoppers to lower the fill heights which were ~17.4 oz in our 16.9 oz bottles. That seemed to work well.

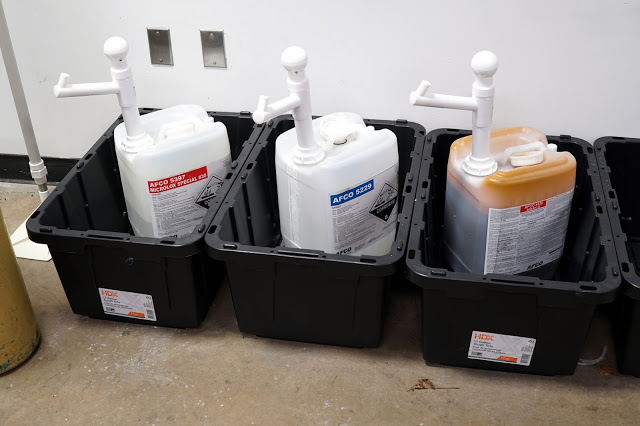
When it comes to cleaning and sanitizing though, we've had to relearn the entire process. You really can't fill a fermentor with 360 gallon of Oxiclean Free and soak overnight or swirl and scrub... I miss those days. First, let's talk about chemicals and what they do. Our main supplier is AFCO, but Berko, Five-Star, and Loeffler all have fans. Prices seemed similar, we just didn't think about ordering until a couple weeks before we started brewing and picked the one with the quickest turnaround time. We buy most of the chemicals in 5 gallon jugs, and pump them into beakers to measure and dose.
Chemicals
Caustic (5229 Caustic) - Caustic is the primary cleaner used by most breweries. Usually sodium hydroxide based and heavily alkaline. It is ideal for breaking down and removing organic deposits (e.g., krausen rings). You can do a bit of trading-off between time, temperature, pressure, and concentration. That said, 2-3% caustic at ~150F (66C) for 20-30 minutes through the sprayball has been a pretty good place to start for us. Caustic is dangerous because it is capable of breaking down your skin (the lye used in soap making is similar). We started with a powdered caustic (Wash-It), but given the price and efficacy we transitioned to liquid.
Phosphoric-Nitric Acid Blend (5397 Microlex Special 30) - Acid helps to remove inorganic deposits, i.e., beerstone (calcium oxalate). It also helps to neutralize any residual caustic (not that there should be any with adequate rinsing) and to passivate stainless steel. Acid blend is used at similar temperatures and cycle lengths as caustic, although slightly cooler, ~130F (54C).
Five Star Peroxyacetic Acid (PAA) - While there are many sanitizers available, PAA is the most popular for breweries. At the right concentrations it is a robust sanitizer with high effectiveness. It breaks down to acetic acid, so it can be used no-rinse. It is a powerful oxidizer, which makes it important to drain any residual before fermented beer enters a tank or keg. Our bucket was leftover from the old brewery in our space, so we bought a pack of test strips and it still reads the expected concentration after dilution.
Five Star PBW - We have a bucket of this alkaline powered cleaner for soaking hot-side equipment and other gear where we don't want to have to be as careful as we would with caustic. We both used it at home, so were more comfortable with it than the Chlorinated Manual Cleaner we started with.
Iodophor (4330 Spark I2) - Similar to the PBW, it is nice to have a less hazardous sanitizer for spraying ports or soaking fittings. It is only effective on clean surfaces, so it is important to remove of detritus before expecting it to work.
Grain Alcohol - Given its quick kill times and evaporation ethanol is the ideal sanitizer for spray bottles and any surfaces that are highly sensitive (e.g., yeast culturing). Isopropyl alcohol is another option.
General Concepts
Pre-Heating - At this scale a tank has so much thermal mass that you can't simply put 15 gallons (57 L) of hot water to a tank and expect it to still be hot after circulating. As a result if you want the caustic or acid to stay hot, you need to pray hot water into the tank. A tank with an electric element (like our keg washer has) helps too.
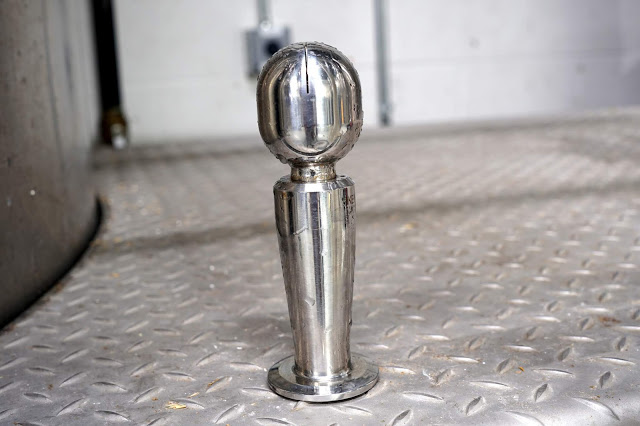
Sprayball - Most tanks have a port that leads to a sprayball, a small metal orb that spins and sprays when liquid is forced through. These aren't always perfect, and can have blind spots, especially in ports and above it. In addition, it isn't effective at cleaning its own exterior.
Passivation - This is what makes stainless steel stainless, a thin layer of chromium atoms at the surface that prevents iron from rusting or leeching into the beer (which weakens the equipment and shortens its lifespan). With a pristinely clean surface, the oxygen in the atmosphere is enough to accomplish this, but acids (especially nitric) are more effective.
Safety
These chemicals aren't anything to joke about. Many brewers have scars gained from caustic or acid dripping onto their skin . Safety glasses, long gloves, chemical resistant boots and pants are a must when handling them. Read the safety data sheet for each chemical you are using and know what to do if some gets on your skin or in your eyes. I don't get to drink as much beer as I used to because the end of the day is usually the most dangerous time.
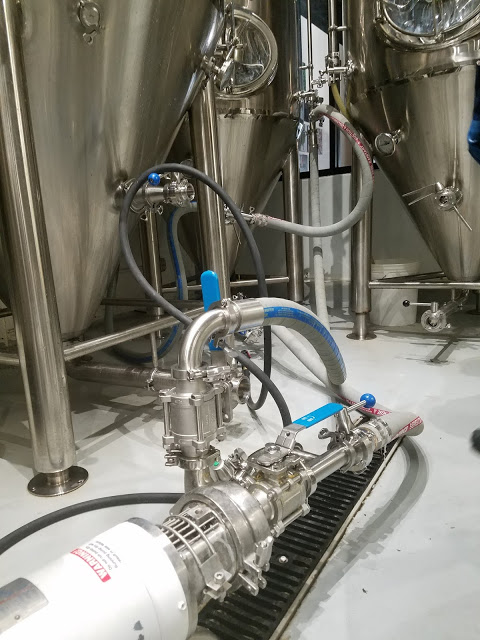
Scott and I prefer to have all of the tank's arms connected from the start, allowing us to use valves to direct the flow of the cleaning and sanitizing solutions. We started off using a manifold coming off the pump, but have changed to daisy-chained T's between the arms. Many brewers prefer to simply move a single output line from the pump between the arms. This requires less setup time, but more active effort once cleaning begins (moving the hose from arm to arm ~10 times through the process). It also carries additional risks if you move the hose without closing a valve.
Our Fermentor CIP Process
1. Once the beer is out of a tank, we turn off the glycol jackets and open the dump valve. We then shoot high-pressure cold water through the sprayball to remove most of the hops/yeast struck to the sides and bottom.
2. We use our on-demand hot water heater to generate 130F (54C) water to spray through the sprayball and manually through a hose to dislodge the bulk of the crud stuck to the sides/top of the fermentor. We'll run it through the pump to get good coverage.
3. We briefly remove the lower fittings on the tanks (including manway, racking arm, thermometer, sample port) to spray out the trub caught in them.
4. We blow compressed air through the sprayball at ~30 PSI with the bottom valve open for 30 minutes. CO2 neutralizes caustic, so best to remove as much as possible before proceeding. This long is likely overkill for a 10 bbl tank, but can't hurt.
5. We assemble our cleaning rig, usually a pump running to the sprayball, with a T to connect it to the racking arm and another to the blow-off.
5. We preheat the tank for a couple minutes by spraying 160F (71C) water in and letting it drain. We hook the water line in right before the pump so we can immediately go to cleaning once it is preheated. Our goal is to get the tank to read ~130F (54C).
6. We then use the hot water heater's built-in meter to send 10-15 gallons of 160F (71C) water into the tank. We dose in 3 oz of caustic per gallon (2.3%) using a stainless steel elbow on one of the ports (chasing the caustic with water to ensure it get in). We then turn the elbow down to allow that port to equalize the pressure inside the tank, while preventing caustic from spitting out.
7. I like to send a little flow through the blow-off and racking arm first to soak them during the 20-25 minutes sprayball at full pressure (60 hz on our pump - or a bit slower if it cavitates). Then five minutes through the other arms, before a final five through the sprayball.
6. Dump the caustic. Rinse each arm with hot water, then burst rinse 10 times for 10 seconds at 130F (54C) through the sprayball, allowing it to drain before each successive rinse. I'll often put 10-15 gallons (38-57 L) into the tank once or twice and recirculate at the end to make sure there is enough pressure to spray all the surfaces. You can check the pH of the drained rinse water to ensure it has returned close normal before proceeding.
2. We then take off all of the fittings (including the sprayball itself), soak them in PBW or caustic. We inspect the fittings and gaskets, rinse and put into a bucket of iodophor. For the ports we spray, scrub and spritz with iodophor before reassembling. We also take the chance to inspect the interior with a flashlight to ensure there are no deposits.
7. We run acid blend at 2 oz per gallon (1.5% by volume) using roughly the same process and times as the caustic. Significantly higher concentrations should be used on new equipment and once a year to ensure adequate passivation.
8. Usually we'll air-dry at this point unless we need the tank the following day. In that case we'll rinse and then sanitize with peroxyacetic acid in cool water at 200 PPM using the same rig, and pressurize the tank to 4 PSI of CO2 to ensure it holds. The next morning we'll dump any residual sanitizer from each port before running wort or beer in.
The whole process including sanitation takes three hours, but most of that time isn't active (just waiting for a purge, or cycle). Going longer on any of the times isn't a big deal, so it is easy to run while working on other things if you keep track of your progress and don't miss a step.
We haven't gotten a CIP cart with dedicated vessels and pump, so our biggest issue currently is that it is difficult for one of us to clean a tank while the other person brews because they require some of the same equipment. Luckily our current schedule of two batches a week doesn't make that too much of an issue.
I am by no means holding this up as a perfect or ideal process. It'll likely be viewed as overkill by some, and inadequate by others. But if you have constructive suggestions, I'd love to hear them! I'd rather err towards overkill because we're dealing with several yeast strains (including killer wine yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae var. diastaticus, not to mention Brettanomyces and Pediococcus in a dedicated tank), although we do have the advantage of only dealing with kegs stored cold.
Other Pieces
We addition we'll pump the same chemicals through our heat exchanger and carbonation stone. For the heat exchanger we also heat pasteurize by running 180F (82C) water for 20 minutes inline once we assemble our knock-out rig (we discard the water until we see wort before sending to the fermentor). Our keg cleaner automatically does the same process on our sanke kegs, including air and CO2 purges to recapture the caustic and sanitizer.
My homebrewing-rate has slowed dramatically the last couple months, not coincidentally we brewed our first batch at the brewery around that time (House Saison brew day). Part of that is brewing 10 bbls about twice a week, the rest is how much time I spend at the brewery doing other stuff. My plan for The Mad Fermentationist is to keep up the same style of post, with recipes and tasting notes for occasional Sapwood Cellars beers. I'll still document homebrew batches when I can, mostly test batches or experiments with impractically weird ingredients.
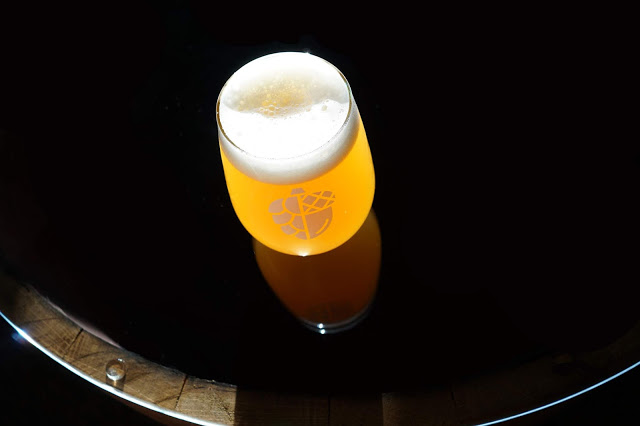
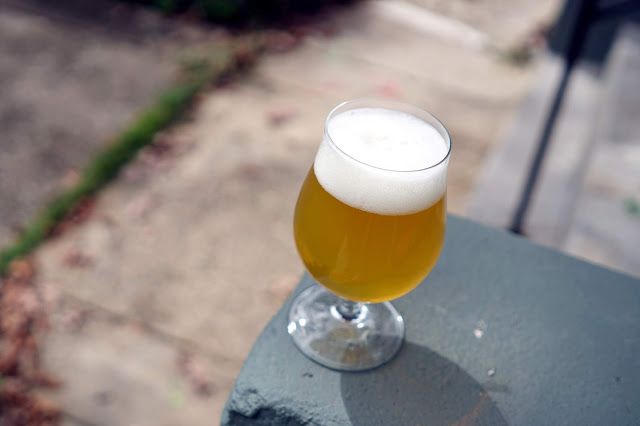
The first beer I wanted to cover is my favorite of the initial four clean batches, Rings of Light. For those interested the name, is a subtle The Fellowship of the Rings reference: "They watched the pale rings of light round his lanterns as they dwindled into the foggy night." It is exactly the sort of beer I love drinking, moderate alcohol (4.8% ABV), but with a huge hop flavor and aroma and a surprisingly luscious mouthfeel. Luckily Untappd reviews have been pretty positive, and it is our tasting room's top seller so far!
You'll likely recognize most of the elements of the recipe as things Scott and I have been doing for years. Golden Naked Oats, Chit malt, Boddington's yeast (RVA Manchester), moderate-high chloride and sulfate, less expensive hops in the boil (Cascade and Columbus), and Citra dry-hopping. We added mid-late fermentation additions to several of our other batches, but this one was soft-crashed to 58F before dry hopping so we could harvest the yeast for re-pitching into an IPA (Cheater Hops) and DIPA (Uncontrollable Laughter).
The process tweaks have mostly been to account for the differences related to the physics of working at scale. For example, usually I'd add a small dose of hops at 15 minutes to up the bitterness, but in this case the extended contact after flame-out makes that unnecessary (between whirlpool, settling, and run-off near-boiling wort is in contact with hops for more than a hour). In fact, we added one barrel of cold water at flame-out to lower the whirlpool temperature to reduce isomerization. Beersmith 3 includes the capability to specify the average temperature of the wort during the whirlpool, still the estimate seems to be wildly higher than the perceived bitterness. I wonder if the hops settling, mixing with the proteins in the trub-cone slows the isomerization rate?
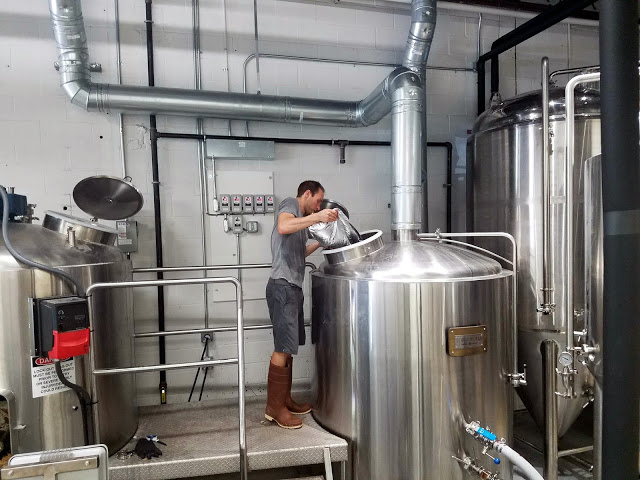
It has taken a little time to dial in our Forgeworks brew house. We achieved slightly lower efficiency and attenuation on this batch than expected for example. We've made a few mistakes and miscalculations along the way, but given neither of us had brewed frequently at a commercial scale I'm happy to report that things have been relatively smooth. Our biggest issues have been with the durability of the equipment itself. For example the rakes in the mash tun detached from the motor twice, and our burner shorted after a boil-over. What is taking the most effort to optimize is our cleaning and sanitation regimen.

Thanks to everyone who came out to our grand opening last weekend! I didn't expect as many fans of the blog to drive from an hour or more away to try the beers and say hello. Either Scott or I will be there most of the time we're open, so let us know! Happy to show you around and talk brewing. For those further away, I'm also running the brewery's Twitter and Facebook accounts for now (Scott took Instagram because I couldn't figure it out).
Rings of Light
Smell – Pleasantly mango-melon hop aroma. As it approaches room temperature I get a slightly toasty-vanilla-richness thanks to the yeast playing off the Golden Naked Oats. Otherwise a pretty clean/fresh aroma.
Appearance – Pleasantly hazy yellow, glowing in the right lighting. I guess we did an adequate job avoiding oxygen pickup during transfers and kegging as it hasn’t darkened! We certainly pulled some hop matter into the bright tank, but it mostly settled out and stayed behind when we kegged, as I don’t see any particulate in the pour. Head is really thick, but could have better retention.
Taste – I really love the flavor on this, really saturated with juicy hops. Similar to the aroma, the tropical flavors from the Citra dominate the Cascade and Columbus. We were surprised how hop-forward it was even before dry hopping (perhaps thanks to the deep kettle slowing the evaporation of the oils?). Bitterness is pleasant, but restrained. Well below the estimated 70+ IBUs, more like 40-50 to my palate.
Mouthfeel – Full bodied, especially for a sub-5% beer. That is thanks to the oats, and low attenuation (which allowed for more malt for the given alcohol). As usually the substantial texture of the head from the chit malt really enhances the perception of creaminess.
Drinkability & Notes – Glad this beer ended up as an early-fall release. It is a little full for a quenching summer pale ale, but it is perfect for temperate weather. The hops are well balanced, and provide enough interest to demand each additional sip. The malt mostly stays hidden, while providing adequate support.
Changes for Next Time – We’ve already got a new batch of this fermenting with the same grist and kettle-hops, although given the tweaks (higher original gravity and different yeast: Lallemand New England and S-04) it may receive a different name.
Recipe
Batch Size: 315.00 gal
SRM: 4.9
IBU: 73.7
OG: 1.052
FG: 1.018
ABV: 4.8%
Final pH: 4.54
Brewhouse Efficiency: 68%
Boil Time: 60 Mins
Fermentables
-----------------
75% - 495 lbs Rahr 2-Row Brewer's Malt
16.7% - 110 lbs Simpsons Golden Naked Oats
8.3% - 55 lbs Best Chit Malt
Mash
-------
Mash In - 60 min @ 153F
Hops
-------
11 lbs Cascade (Pellets, 7.20% AA) - Steep/Whirlpool 75.0 min
11 lbs Columbus (Pellets, 15.70% AA) - Steep/Whirlpool 75.0 min
22 lbs Citra (Pellets, 12.00% AA) - Dry Hop Day 10
Other
-------
40 g Whirlfloc G @ 15 mins
Water
-------
200 ml Phosphoric Acid 75% @ Mash
1.00 lb Calcium Chloride @ Mash
0.70 lb Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate) @ Mash
50 ml Phosphoric Acid 75% @ Sparge
Calcium | Chloride | Sulfate | Sodium | Magnesium | Carbonate |
120 | 150 | 100 | 20 | 5 | 100 |
Yeast
-------
RVA Manchester Ale #132
Notes
-------
Brewed 8/29/18
Collected 315 gallons of water.
All salts and 100 ml acid right after mash-in. Ran rakes for 15 minutes, started recirculation 10 minutes after mash in. After 10 min of recirculation, measured temp at 152.8F.
Measured mash pH at 5.42, add 50 mL more acid. 5.39, add 50 mL more acid. 5.34.
Sparge water 183F, pH 6.47 with acid addition - more next time
Start of boil with 11 bbls of 1.055 runnings.
Added 1 bbl of cold water at the start of the whirlpool. Combined temperature 196F, added hops.
Run-off started at 66F. .5L/min of O2 through in-line stone.
Ended up with a wort temperature of 64F. Set tank to to 66F. By the next morning the glycol chiller had popped the breaker and the tank was at 69F... Reset and lowered to 67F.
8/31 Raised set-point to 69F to ensure finish.
9/3 Fermentation appears nearly complete from lack of CO2 production. Tastes good, better hop aroma than expected. Up to 70F to ensure it is done before soft crashing.
9/6 Harvested yeast. Left blow-off open so no dissolved CO2.
9/7 Dry hopped with 22 lbs of Citra through the top port while running 25 PSI of CO2 and blow-off arm closed. Closed everything and add 5 PSI as head pressure.
9/8 Pushed 15 PSI through racking arm for 1 minute to rouse, 18 hours after dry hopping. Dropped temperature to 54F.
9/9 Pushed 15 PSI through racking arm for 1 minute. Dropped temperature to 50F.
9/10 Crashed to 36F.
9/12 Moved to bright tank. 3 L/min of CO2 set to 16 PSI got to ~11 PSI at 36 F. 2.6 volumes of CO2 prior to kegging.
9/15 Kegged, 17 kegs with the last almost full.
I get a commission if you buy something after clicking the links to MoreBeer/Amazon/Adventures in Homebrewing/Great Fermentations!
I have nothing against brewing to-style. You can make magnificent and delicious beers by using ingredients from a single region with the goal of a classic balance. That isn't who I am as a brewer though. The recipe for Sapwood Cellars' False Dragon is the sort that I'm passionate about. We selected ingredients from all over the globe to create a flavors and aromas that aren't authentic to any one tradition. What I wanted was an earthy-crisp malt flavor, a white-winey hop aroma (for less money than Nelson Sauvin), and a subtle spicy and fruity-boost from the yeast without getting in the way. That required malts from America and England, hops from America and Germany, and yeast from England and Belgium.
I'd been experimenting with the hop bill for a few months to get the ratio right, and eventually settled on 2:1 in favor of Mosaic. After a few test batches, Scott and I have embraced adding less expensive hops on the hot-side (Cascade, Columbus, Chinook, Centennial etc.) with the more aromatic and expensive varieties saved for the fermentor. I wanted to split my homebrewed test batch to compare S-04 alone against S-04 with 8% T-58. As with Ziparillo, dry yeast is cost-effective especially if you can't repitch thanks to early or mid-fermentation dry hopping. Belgian strains have shown heightened biotranformation abilities is some studies, so it seemed like a good candidate for double dry-hopping.
For the 10 bbl batch we decided to fill-in a gap in our range when the first batch of Rings of Light (our Citra dry-hopped hazy pale ale) came in under-alcohol at 4.8% thanks to lower-than-expected efficiency. In effect the two recipes switched places with False Dragon becoming the "bigger" pale ale at 5.3% rather than the 4.7% of the test batch. Our attenuation has been lower than expected across the board for our first five batches too. We're still trying to figure out the cause given it has happened with multiple yeast strains - likely mash related. Luckily our hop flavor and aroma have both been wildly better than either Scott or I have been able to achieve at home, I'm sure surface-to-volume ratio plays a role.
Your first chance to try this beer is at the Sapwood Cellars grand opening, Noon-10 PM on Saturday 9/29. We'll be open Thursday-Friday 4-10 PM and Saturdays Noon-10 PM from then on. Stop in, drink a beer, say hello!
The name False Dragon come from The Wheel of Time series of books by Robert Jordan. My commute has gone from 20 minutes on the subway to my desk job to ~40 minutes by car. Audio books are my new friend. While I'm sure brewing podcasts would be a more productive use of my time, after 12 hours brewing it is nice to have a little escapism.
False Dragon S-04
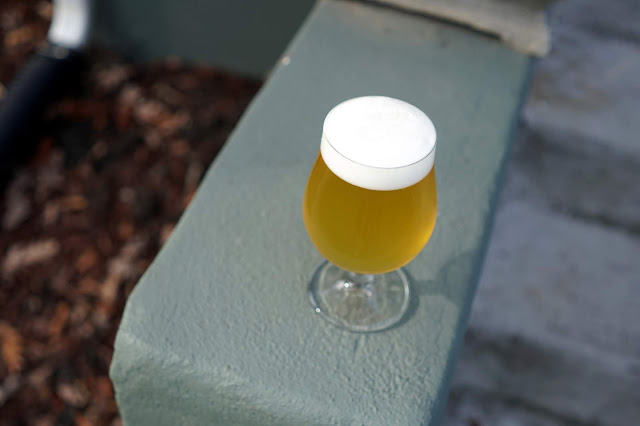
Smell – Had to go for a fresh pour after taking photos as it had gone a hint skunky after five minutes in the sun… Nose is a fresh “true” hop aroma to the Mosaic and Hallertau Blanc. White wine, but also some blueberry and green/herbaceous. Certainly Nelson-reminiscent, but a unique character as well.
Appearance – Pale yellow, pleasantly hazy. Good head and lacing, but the foam itself feels airy on the tongue. I guess I’ve gotten used (and miss) to the contribution of chit malt.
Taste – A firm amount of bitterness in the finish, but it doesn’t linger. Light and bright with the tropical-fruity hops starring. Rye doesn’t really make a strong showing, although I’ve always found it more subtle than some others taste.
Mouthfeel – The rye helps prevent it from being watery, but it is a summery pale ale. Glad we ended up a little higher OG/FG on the big batch. Medium carbonation, nice for a lighter beer.
Drinkability & Notes – A pleasant session IPA. The Mosaic and Hallertau Blanc work better together than apart.
Changes for Next Time – 10% chit in place of the base malt wouldn’t hurt. Could certainly up the rye too for a bigger contribution.
S-04 and T-58
Smell – More rounded, less grassy-distinct hop aroma. Tropical, juicy, inviting. The green flavors are now more honeydew melon. Impossible to say how much of that is actual hop chemical reaction, or synergistic between the hops and esters. Lightly bready.
Appearance – Looks similar in terms of head, color, and clarity.
Taste – Lower perceived bitterness. A more saturated/integrated fruity hop flavor. Passionfruit especially. I think this is the more approachable and interesting beer, and distinct from the other English-only fermentation we are doing (using RVA Manchester). Slightly elevated phenols, but much lower than from the WB-06 in Ziparillo.
Mouthfeel – Slightly creamier (perhaps just the lower perceived bitterness?), identical carbonation.
Drinkability & Notes – I was able to identify these pretty easily in a blind tasting. It is amazing how much impact such a small amount of yeast can make.
Changes for Next Time – We decided to back down the T-58 4.4% of the blend to allow a bit more of that fresh/distinct hop character through. Other than the higher gravity, the recipe was otherwise unchanged for the 315 gallon batch! We’ll probably up the rye for batch #2 now that we know we can handle higher percentages of high beta-glucan huskless grains.
False Dragon - Test Batch
Batch Size: 11.00 gal
SRM: 4.1
IBU: 30.0
OG: 1.046
FG: 1.012/1.012
ABV: 4.7%
Final pH: 4.43/4.49
Brewhouse Efficiency: 72%
Boil Time: 60 mins
Fermentables
-----------------
75.6% - 17 lbs Rahr 2-Row Brewer's Malt
14.4% - 3.25 lbs Briess Rye Malt
10.0 % - 2.25 lbs Crisp Floor Malted Maris Otter
Mash
-------
Mash In - 45 min @ 156F
Hops
-------
8.00 oz Centennial (Pellet, 7.20%) @ 30 min Steep/Whirlpool
6.00 oz Mosaic (Pellet, 12.25%) @ Dry Hop Day 3
3.00 oz Hallertau Blanc (Pellet, 10.50%) @ Dry Hop Day 3
6.00 oz Mosaic (Pellet, 12.25%) @ Dry Hop Day 7
3.00 oz Hallertau Blanc (Pellet, 10.50%) @ Dry Hop Day 7
Other
-------
1 Whirlfloc Tablet @ 5 mins
Water
-------
18 g Calcium Chloride
12 g Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate)
6 tsp Phosphoric Acid 10%
Calcium | Chloride | Sulfate | Sodium | Magnesium | Carbonate |
150 | 150 | 150 | 15 | 10 | 90 |
Yeast
-------
11.5 g SafAle S-04 English Ale
or
11.5 g SafAle S-04 English Ale
1 g SafBrew T-58 Specialty Ale
Notes
-------
Brewed 8/19/18
Mash pH = 5.44 (at mash temp) after acid additions.
Collected 14.5 gallons of 1.046 runnings.
Added heat to maintain a whirlpool temperature of 200F.
Chilled to 64F. Half with 1 g of T-58 and 11 g of S-04, and half with only 11 g of S-04. Left at 62F ambient to begin fermentation after shaking to aerate.
69F internal temperature during peak fermentation.
8/22 Dry hopped each with 3 oz of Mosaic and 1.5 oz of Hallertau Blanc.
8/27 Second dry hop for both.
9/1 Kegged both, 1.012, moved to fridge to chill.
9/2 Hooked up to gas and tapped to remove sludge. S-04 batch clogged poppet a few times.
I get a commission if you buy something after clicking the links to MoreBeer/Amazon/Adventures in Homebrewing/Great Fermentations!
It is tempting to say that beer isn’t like that. After all, each all-grain batch starts with the four basic ingredients and we do the rest… sure it would be a challenge to grow and malt barley, harvest and dry hops, isolate/propagate wild yeast, and haul water from a local stream, but what vessels would you use to boil/ferment? What about sanitizer, minerals, clarifiers, compressed CO2?
What follows is a high-level overview of what is required to brew a single batch of beer at Sapwood Cellars. Obviously, you could keep digging deeper into each one of these, peeling back layer-after-layer to the inputs of each input (e.g., the shoes that the hop harvester was wearing). I’ll arbitrarily stop where I lose interest. Needless to say though, the work of thousands in not millions of people goes into each of our batches. Scott and I just get the credit (or blame) because we're the ones at the end of the chain!
Ingredients
Water
Our water comes from Liberty Reservoir. From there it goes to Baltimore’s Ashburton water treatment plant. Baltibrew posted a nice series on the Baltimore water system. Luckily for us the existing minerals are mostly beneficial to the character of our beer. The carbonate is a bit higher than we’d like, but not by enough to require the waste of reverse osmosis.
Once pipes take it to the brewery it passes through a carbon filter to remove chlorine, and then an on-demand hot water heater. The fuel is natural gas piped into the brewery by BG&E (by way of fracking or older methods, and then refining). From there the water travels through a hose to our hot liquor tank where an electric element allows us to adjust the temperature. The electricity comes from a mix of fossil fuels, nuclear, and ~5% renewables.
To adjust the mineral content of the water, we add calcium chloride (from limestone-hydrochloric acid reaction or natural brine concentration) and calcium sulfate (harvested and refined from gypsum rock deposits). In addition, we add 75% phosphoric acid to adjust the pH of the water. Phosphoric acid is usually produced by combustion, hydration, and demisted from three ingredients: phosphorus, air, and water.
Grains
The grain we mash is a mixture of barley, wheat, oats, and rye depending on the beer. These are grown primarily on farms in North America and Europe. It is then soaked, sprouted, dried, and kilned by a maltster. The precise equipment required varies by malt and producer. In some cases it is a large industrial operation, in others the malt is still manually turned. The bulk of our base malt is Rahr brewer’s 2-row from Minnesota, but in our first order we also had sacks from Briess, Chateau, Simpsons, Crisp, Best etc. Most of the unmalted flaked grains (steamed and rolled to gelatinize their starches) are from Grain Millers.
We decided to hold-off on buying our own mill, to save the cost at the start… but after a few brews I can say a mill and auger are in our near future. We order our grains from Brewers Supply Group, which pre-mills the grain. We also occasionally add a few sacks to a Maryland Homebrew order from Country Malt.
Once we’re done with the now “spent” grain, they are picked-up by Keith of Porch View Farms. He feeds it to his animals as most of the carbohydrates are extracted into the wort, but proteins remain.
Hops
Our hops are grown throughout the higher latitudes of the globe, primarily the Pacific Northwest of the United States, but also Australia, Germany, and Czech Republic. The hops are first stripped from their bines, dried in an oast, and then baled. After selection, various lots are blended to create a consistent product and the hops are pulverized and pelletized. They are then vacuum-packed in mylar and stored cold to preserve their aromatics. Our hops primarily came from Hop Havoc, but we’re working on getting contracts for the upcoming harvest.
Yeast
Most of the yeast we’re using are the decedents of yeast that have been fermenting beer for hundreds or thousands of years. A couple hundred years ago their ancestors were part of a mixed-culture at breweries in England and Belgium, only to be lucky (and talented) enough to be isolated as a pure culture that gained success. Our Saccharomyces cerevisiae so far has come from RVA, Fermentis, and Lallemand for our “clean” beers. These needed to be isolated, propagated, and in some cases dried.
The sour and wild beers are too complex to track. They come from labs, bottle dregs, and a house culture. They may have come via a barrel, the breeze, an insect, or any number of other vectors into a brewery or labs. For example the Hanseniaspora vineae we are fermenting a hoppy sour for Denizen's Make It Funky festival came from Wild Pitch Yeast which isolated it from tree bark.
Fruit
We don’t have any beers far enough along for fruit, but we’re planning to source as much of it as we can directly from local farms and orchards. Most fruit is at its best when it is picked ripe and used quickly. I'm sure we'll use dried fruit, aseptic purees, juices, and freeze-dried fruits depending on quality, availability, and desired results as well. The first batch will probably be a tart saison on grape pumace (the pressed skins) from a local natural winery.
Other Consumables
Gas
Carbon dioxide is usually produced as a byproduct of some other activity (e.g., hydrocarbon processing). Our CO2 is stored in a 750 lb tank in a liquid state. We use it to carbonate and serve beer. It isn't economical at our scale to recapture the CO2 released by fermentation. Our supplier is Robert’s Oxygen.
As the air on Earth is 70% nitrogen it is usually concentrated with the use of a nitrogen generator. These rely on a membrane that allows nitrogen through. We need nitrogen to help push the beer through the long-lines from our walk-in to the tasting room (pure CO2 would lead to over-carbonation at those pressures). As the second most abundant gas in the atmosphere, oxygen generation uses similar technologies. We pump .5L/minute into the wort as it exits the heat exchanger, the yeast quickly uses it to create sterols for healthy cell walls when they bud. We get these two gases in large cylinders that are swapped out.
Chemicals
We need cleaners like caustic (sodium hydroxide) to remove organic deposits, and a phosphoric-nitric acid blend to remove inorganic beer stone and passivate the stainless steel. For sanitation we use iodophor for fittings in buckets, and peracetic acid for the tanks. These are made in a variety of industrial processes that I’m totally unaware of. Our chemicals are provided by Zep/AFCO.
Clarifier
Whirlfloc G helps proteins clump together in the last 15 minutes of the boil to be left behind. It is derived from Irish moss (seaweed) that is dried and granulated. As a vegan brewery, no gelatin or isinglass for us.
Barrels
Oak barrels start as oak trees. They are processed into planks, and then purchased by a cooperage which dries (either in a kiln or naturally). They are then assembled into barrels with metal hops, toasted, and sealed. From there they go to vineyards and distilleries that age their products in them. Beer is best in barrels that have already lost much of their oak character, so we buy them from other producers. A small amount of the wine or spirit is still present in the wood, providing a moderate contribution to the first batch, diminishing with each additional batch.
Equipment
The stainless steal for the vast majority of our equipment comes from China. Our brewhouse was constructed by Forgeworks in Colorado. Our fermentors and bright tank from Apex and DME in China. Our keg washer from Colorado Brewing.
The cooling of the fermentors is accomplished by a glycol chiller from G&D Chillers in Oregon. The ethylene glycol itself comes from ethylene and oxygen. The chiller also assists chilling the wort with our two-stage Thermaline heat exchanger (primarily more stainless steel). The copper pipes that carry the glycol are insulated with Armaflex. The flow of the glycol to individual tanks is controlled by electronic temperature sensors and solenoid valves.
Other equipment includes hydrometer, refractometer, pH meter, hoses, gaskets, and all manner of other valves and fittings.
For the space itself there was already plenty of concrete, bricks and metal. We hired Kolb Electric and B&B Pipefitters to do the installation of the bulk of the wires, pipes, and connections.
There is also everything that goes into serving a beer once it is ready. Kegs (Corny kegs for the sours and infusions, sanke for the standard clean beers), stainless steel fittings, beer lines, glasses (including the printed logo and the glasswasher) etc.
What’s the Point?
I don’t really have one. To me it is just remarkable how much of the complexity of brewing a batch of beer is now hidden in the inputs. I know how to brew beer at my house or a brewery, but if you put me out in the woods even with all the ingredients, I couldn’t brew a batch. Thinking about what is required for each batch makes me appreciate how nice it is to live in a time when I can brew beer as simply as going online and ordering the equipment and ingredients I want. It also shows me how much I still have to learn about making beer.
At the same time, it means that beers everywhere are mostly separated by the choices the brewer makes rather than the availability of ingredients. The exchange of information accelerated by the Internet. I hope there continue to be regional variations, specialties, and preferences. Traveling isn't as exciting when everyone brews NEIPA and pastry stouts.
Dry hopping mid-fermentation is a great technique for chasing away raw-green hop aromatics that turn-off some drinkers. The problem is that adding hops early makes harvesting yeast far more difficult. Our solution was to use dried yeast. For a fraction of the price of a liquid pitch (~$60 for 500 g dried) it means we don't feel bad not cropping and repitching. Dry yeast also allows for easy strain blending by weight. In this case the test batch was 85% S-04 and 15% WB-06. The goal was to support the fruity hops with a little banana from the hefeweizen strain. An idea I first tried in my American Oat Ale.
The grist is a callback to what we developed for Modern Times Fortunate Islands, still my favorite of their regular offerings. The grains were in turn inspired by Three Floyds Gumballhead. We decided to go a bit lighter on the wheat until we get used to how large amounts of huskless grains lauter on our Forgeworks brewhouse. Hot-side hopping is a single dose of Cascade in the whirlpool. A classic variety with a good blend of oils, but without excessive alpha acids (or cost). Despite that, for the up-scale we're going to lower the whirlpool temperature to ~195F with a barrel of cold water at flame-out to keep the IBUs under 20. Dry hopping with Amarillo for stonefruit aroma.
Hefeweizen yeast, CaraVienna, Cascade, and Amarillo is a combination I tried back in 2010 for this Hoppy Hefeweizen. Not the same intended balance on that batch, but a similar palate of flavors.

The wrinkle in this test batch was that I split it pre-boil. I've been editing Scott's draft for "The New IPA" and the research suggested that many hop oils peak very quickly at higher temperatures and then dissipate. So I split the batch, half with a 20 IBU addition at 60 minutes followed by a flame-out addition immediately after turning on the immersion chiller. The other half I added a hop-stand/whirlpool addition allowing it to sit for 45 minutes before starting the chill. I even left the heat on low to better replicate the slow cooling of a commercial-scale whirlpool.
Going in I was suspicious. I'd changed from quick-chilling to hop-stands a few years ago, and felt that my beers had gotten a better more saturated hop flavor. The beers came out surprisingly similar, but not exactly the same.
Ziparillo - Quick Chill
Smell – Clean yeasty-doughy nose. Banana. Cascade grapefruitiness shines through as the dominant hop character. Certainly reminds me most of hoppy hefeweizens that I’ve brewed previously. Surprising how much yeast character there is from a low percentage of WB-06.
Appearance – Pale-gold, mildly hazy of the standard hefeweizen type. Not milky-haze. Good head retention and cling.
Taste – Bitterness is present, a bit higher than 20 IBUs in my estimate. Crisp finish with some lingering hop resin. Amarillo comes in a bit towards the end, apricot. Odd that I get the kettle hops in the nose and the dry hops in the flavor. The quick chill seems to have imparted a more dry-hop like character. Dry, with a finish that reminds me of some sort of herbal spritzer?
Mouthfeel – Snappy, good firm carbonation, but not as high as a traditional hefe. Dry, slightly tannic finish.
Drinkability & Notes – A nice session beer. The polyphenols from the early-boil addition may be making the bitterness come-across higher than the calculated IBUs would suggest.
Changes for Next Time – Drop the bittering addition to 10 IBUs, and this would be much closer to the balance I was looking for. Nice as is, but likely too bitter for many hop-phobes. Yeast character is a bit distracting.
Ziparillo - Hop Stand
Smell – Similar, but the yeast character comes across as leaning more bubblegum than banana. Slightly more phenolic as well, peppery. Hops are better integrated into the yeast character or maybe just less assertive. I get honeydew melon.
Appearance – Identical. In this case the timing of the boil hops and speed of chilling doesn’t seem to have effected clarity.
Taste – Bitterness seems lower/smoother, and the finish rounder despite the same calculated IBUs. Like the nose the line between fruity yeast and hops is less distinct than the other version. There is more banana than in the nose, but it is still relatively subdued. Hops are bright and citrusy.
Mouthfeel – Smoother, less tannic. Coating compared to the other half. That isn’t a character that necessarily sounds beneficial to a session beer, but in this case it makes it easier and more pleasant to drink.
Drinkability & Notes – Closer to what I was looking for, the hops and yeast meld together into a pleasant fruit salad. Rather than a generic fruitiness throughout the effect is different flavors from nose and mouth, evolving as it warms. One friend noted that it has sort of an Allagash White thing going on, which was exactly my intent.
Changes for Next Time – We’ll be cutting the WB-06 from 15% to 7.5% in the big batch. The taller fermentor should suppress ester production as well. We’ll add a barrel of cold water at the end of the boil to lower the temperature and further smooth the hop bitterness contributed by the whirlpool addition.
Recipe
Batch Size: 12.00 gal
SRM: 4.8
IBU: 18.3
OG: 1.048
FG: 1.008
ABV: 5.25%
Final pH: 4.60
Brewhouse Efficiency: 72%
Boil Time: 60 mins
Fermentables
-----------------
68.2 % - 15 lbs Rahr 2-Row Brewer's Malt
22.7 % - 5 lbs Briess Red Wheat Malt
6.8 % - 1.5 lbs Briess Caravienne
2.3% - .5 lbs Rice Hulls
Mash
-------
Mash In - 45 min @ 158F
Hops
-------
V1
1.00 oz Cascade (Pellets, 5.5% AA) @ 60 min
3.50 oz Cascade (Pellets, 5.5% AA) @ Flame-Out
2.00 oz Amarillo (Pellets, 9.2% AA) @ Dry Hop Day 2
V2
3.50 oz Cascade (Pellets, 5.5% AA) @ Whirlpool 45 min
2.00 oz Amarillo (Pellets, 9.2% AA) @ Dry Hop Day 2
Other
--------
1 Whirlfloc Tablet @ 5 min
Water
-------
18.00 g Calcium Chloride
5.50 g Gypsum (Calcium Sulfate)
9.00 tsp Phosphoric Acid 10%
Calcium | Chloride | Sulfate | Sodium | Magnesium | Carbonate |
140 | 170 | 100 | 15 | 10 | 90 |
Yeast
-------
22 g SafAle English Ale S-04
4 g Safbrew Wheat WB-06
Notes
-------
Brewed 8/5/18
5.28 at mash temperature after all additions (~5.5 corrected to room temperature).
Split between two boils:
1. 1 oz of Cascade @60 min, and 3.5 oz of Cascade with a quick chill at flame-out (added hops right after starting IC).
2. 3.5 oz of Cascade with a whirlpool at 212F (with heat) for 45 minutes... mostly stayed 190-200F.
Chilled to 68F, pitched 1 pack of S-04 and 2 g of WB-06 into each (no rehydration). Shook to aerate.
Same fermentation, beer temp 65F.
8/7/15 Dry hopped ~36 hours after pitching. Set beer temp to 68F to continue fermentation.
Kegged 8/16/18
I get a commission if you buy something after clicking the links to MoreBeer/Amazon/Adventures in Homebrewing/Great Fermentations!