New beer designed to pair with the restaurant group’s contemporary Chinese dishes.
The post Lotus Dining and White Bay team up on rice lager appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
New beer designed to pair with the restaurant group’s contemporary Chinese dishes.
The post Lotus Dining and White Bay team up on rice lager appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Brewery is in the midst of a multi-stage expansion across all areas of operations.
The post Burleigh toast 15 years with expansion and a new beer appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 Michael Fairbrother from Moonlight Meadery joins me this week to discuss honey varieties and mead making. Michael is owner and founder of the award winning Moonlight Meadery. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. […]
Michael Fairbrother from Moonlight Meadery joins me this week to discuss honey varieties and mead making. Michael is owner and founder of the award winning Moonlight Meadery. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. […] Seven Latino men gathered on a Hacienda Heights driveway on a warm Southern California night. Shiny homebrewing equipment filled the garage so the fledgling craft brewers stood in the car port—pint glasses in hand—sharing names, hometowns and brewing experiences. The SoCal Cerveceros homebrew club was born. “We didn’t really know what it was going to […]
The post SoCal Cerveceros, America’s Largest Latino-Based Homebrew Club, Is Making Its Mark appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
“Break even” Helios Brewing now eyeing growth and profitability come July 1.
The post Excise rebate increase a ‘game changer’ for brewery appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 This week I take a look at homebrewing in the modern era, how it has developed and the impact of technology on brewing. A Quick History of Modern Homebrewing While brewing beer at home has been done for many thousands of years, the modern history of homebrewing in the US has some clearly defined dates: […]
This week I take a look at homebrewing in the modern era, how it has developed and the impact of technology on brewing. A Quick History of Modern Homebrewing While brewing beer at home has been done for many thousands of years, the modern history of homebrewing in the US has some clearly defined dates: […] Non-alcoholic craft brewery to ‘raise their goals’ after snaring Amazon grant
The post UpFlow to chase export markets after $200K win appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
This month marks 50 years in brewing for one of Australia’s true icons of beer.
The post Celebrating Chuck Hahn’s 50 years in brewing appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
American craft beers find their way into Japanese and Korean restaurants.
The post Spice, Fat, Acid, Beer appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
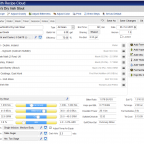 This week I wanted to share a more detailed look at the upcoming Web based version of BeerSmith which is scheduled for release in June of 2021. It will be available to all Gold+ license holders of BeerSmith 3. When released, you can simply log into your existing BeerSmithRecipes.com account and edit recipes in your […]
This week I wanted to share a more detailed look at the upcoming Web based version of BeerSmith which is scheduled for release in June of 2021. It will be available to all Gold+ license holders of BeerSmith 3. When released, you can simply log into your existing BeerSmithRecipes.com account and edit recipes in your […] Malt Shovel Brewers & BentSpoke come together for the third year in a row to […]
The post Brewing in Tandem appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
BentSpoke and Malt Shovel combine again but release comes in cans for first time.
The post New BentShovel beer continues 30 year bond appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Tekapō’s Burkes Brewing’s hazy rates among the top New Zealand beers in 2021.
The post #Fakenews is big news in Burke’s backyard appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Brewery plans to build production facility and restaurant on rural land north of Sydney.
The post WA’s Beerfarm confirms major NSW expansion plans appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
The exclusive line-up of beers and ciders for this weekend’s GABS Sydney event.
The post GABS’ exclusive festival beer and cider list appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Bright Brewery release the DoggoBrau XPA, N.E.V IPA and Fun Socks Talus IPA.
The post Bright days ahead with these new beers appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
A brewery and a winery have found validation in harnessing smoke tainted grapes.
The post Tainted love: Beers give smoky grapes a bright side appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Sydney brewery planning major expansion as target figure fast approaches.
The post Batch on target for $1.5 million crowd fund appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Hit hard by the pandemic, breweries across the country are nonetheless finding ways to give back to their local communities.
The post In the Midst of a Pandemic, Breweries Are Giving Back to their Communities appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
Interest in beer’s provenance sees it released again after being discontinued in 2016.
The post Cascade relaunch First Harvest fresh hop beer appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Brewery wants to see the same program implemented in major retailers nationwide.
The post Bright rolls out PakTech recycling scheme appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Proceeds from sales of the limited edition release will go to various Australian charities.
The post Rolling Stone and Young Henrys release hazy pale appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Cancelled last year, the event returns and is looking to make up for lost time.
The post Good Beer Week’s tenth anniversary program appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
We look at all four of the Into the ‘Wood 2020 releases.
The post Stomping Ground’s Into the ‘Wood – a year in review appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Brewery looking to the positives as their roller coaster taproom journey nears its end.
The post The silver lining of Deeds Brewing’s long wait appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
The limited edition sneakers can be claimed following XPA purchases at selected locations.
The post Coopers and Volley create the XPA shoe appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Tasmania’s Van Dieman Brewing is holding its annual hop picking day this Saturday.
The post Get a hands on approach to making beer appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Deeds Brewing release three hazies including one exclusively with Beer Cartel.
The post The good Deeds continue with three more hazies appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
New margarita gose uses water from nearby beach, pink salt, real agave and lime.
The post Nomad’s Freshie returns in margarita form appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Alcohol free beer is flowing in venues as Australia’s first NA bar opens soon.
The post The heaps normal growth of on-premise NA beer sales appeared first on Beer & Brewer.