Alcohol free beer is flowing in venues as Australia’s first NA bar opens soon.
The post The heaps normal growth of on-premise NA beer sales appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Alcohol free beer is flowing in venues as Australia’s first NA bar opens soon.
The post The heaps normal growth of on-premise NA beer sales appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
The team behind well-known Sydney brewery to open a brewpub in country NSW.
The post Nomad go overland with new Mudgee brewery appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Sydney brewery’s expansion includes new tanks, canning line and dedicated barrel room.
The post Wayward to increase capacity by 25 per cent appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Sales of adjunct-laden, higher alcohol sweeter beers have boomed in Australia.
The post Go big and stay home: the rise of the dessert beer appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
Build Me A Brewery delves into the dos and don’ts so you don’t have to.
The post The ‘reality check’ podcast for start-ups appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 This week I cover mead making fermentation and finishing. Last week in part 1, I provided an overview of mead making and the first steps of making the must, pitching your yeast and adding nutrients. This week I will cover the remaining steps. As I covered last week the key components of modern mead making […]
This week I cover mead making fermentation and finishing. Last week in part 1, I provided an overview of mead making and the first steps of making the must, pitching your yeast and adding nutrients. This week I will cover the remaining steps. As I covered last week the key components of modern mead making […] Canberra brewery create a new sour to celebrate forthcoming art exhibition.
The post Capital Pucker Up with new love potion appeared first on Beer & Brewer.
 This week I take a look at the fundamentals of modern mead making, including staggered mead nutrients, degassing and finishing a mead. Modern Mead Making I started making mead a few years back, and it has been an enjoyable addition to my beer brewing hobby. Most home brewers have the equipment for mead making with […]
This week I take a look at the fundamentals of modern mead making, including staggered mead nutrients, degassing and finishing a mead. Modern Mead Making I started making mead a few years back, and it has been an enjoyable addition to my beer brewing hobby. Most home brewers have the equipment for mead making with […] Celebrate Winter Bonfire Bash Series, Lumberjack Competition, Frying Pan Toss, Return of Husky Hamburger, Flapjacks & Flannel and Much More Highlight 2021 Winter Events Central Virginia’s Stable Craft Brewing at Hermitage Hill, an authentic working farm brewery and winery, is pleased to announce its 2021 January through March special event schedule. Saturday’s will come alive […]
The post Stable Craft Brewing At Hermitage Hill Announces 2021 January – March, 2021 Special Events appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
Brewpubs boost flavor on their menus by pouring their beers into the pizza dough and serving up the perfect slice.
The post Beer-infused Pizza Dough is a Perfect Brewpub Pairing appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
 This week we take a look at some alternative strategies for adding nutrients to your mead for proper fermentation. I also explain the TiONSA and TONSA 3 models which are implemented in BeerSmith. Staggered Nutrient Additions A key part of modern mead making techniques is the staggered addition of mead nutrients. Prior to the adoption […]
This week we take a look at some alternative strategies for adding nutrients to your mead for proper fermentation. I also explain the TiONSA and TONSA 3 models which are implemented in BeerSmith. Staggered Nutrient Additions A key part of modern mead making techniques is the staggered addition of mead nutrients. Prior to the adoption […]  Jeff Bloem joins me from Murphy & Rude Malting to discuss Craft Malting and brewing with Craft Malts. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […]
Jeff Bloem joins me from Murphy & Rude Malting to discuss Craft Malting and brewing with Craft Malts. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […] Solve all of yours (and your dog’s) holiday shopping needs with Stable Craft’s Holiday Gift Cards Central Virginia’s Stable Craft Brewing at Hermitage Hill, an authentic working farm brewery and winery, is making holiday shopping safer and more seamless this season, with the offering of its Stable Craft Holiday Gift cards. In addition to being the perfect […]
The post Stable Craft Brewing’s 2020 Holiday Gift Guide For You And Your Four-Legged BFF appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
The Virginia Beer Company (Williamsburg, VA) will mark the holiday season with the return of their seasonal Spiced Milk Stout, Evil Santa. “Since the first winter we were open back in 2016, Evil Santa has been one of our most sought after recipes,” reminisces Co-Founder Robby Willey. “The branding is playful, the time of year […]
The post Virginia Beer Co. Releases Four Evil Santa Spiced Milk Stout Variants appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
 Mitch Steele joins me this week to discuss brewing low-calorie and low carbohydrate beer as well as seltzer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […]
Mitch Steele joins me this week to discuss brewing low-calorie and low carbohydrate beer as well as seltzer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […] In August 2020, the federal Food & Drug Administration (FDA) finalized the definition and labeling requirements of gluten-free fermented and hydrolyzed foods (including beer and other alcoholic beverages). The ruling provides a clear delineation between products that are truly gluten-free and products that are not and how product labels communicate those differences to consumers. In […]
The post Gluten-Free Brewers Group Responds to FDA Final Rule on Gluten-Free Claims on Fermented Foods appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
San Diego, CA (October 22, 2020) – PourMyBeer partners with Tappizza, San Diego’s latest pizza destination, to provide the ultimate pizza and beer experience with a 21-tap self-serve beer and hard seltzer beverage wall. Tappizza, located at 8242 Mira Mesa Blvd, is elevating the dining experience by putting its customers in control of their drinks, […]
The post San Diego Now Home to a Pizza and PourMyBeer Haven appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
 Gordon Strong joins me for a discussion on German Lager beer styles and some tips for making the perfect lager. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio […]
Gordon Strong joins me for a discussion on German Lager beer styles and some tips for making the perfect lager. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio […]  This week I take a look at methods for doing sensory analysis of hops as well as some of the resources available to understand hop flavor and aroma better. Understanding Hop Flavor and Aroma For a few years now I’ve been doing presentations on beer recipe design where I encourage brewers to get more familiar […]
This week I take a look at methods for doing sensory analysis of hops as well as some of the resources available to understand hop flavor and aroma better. Understanding Hop Flavor and Aroma For a few years now I’ve been doing presentations on beer recipe design where I encourage brewers to get more familiar […] Fall is in the air and that means one thing: harvest season! Brewing with fresh hops is a meticulous process, having to rely on bountiful bines and timing of wet hops plucked, packaged, and shipped overnight via air freight to align with a brew day built around the arrival of those hops and those hops alone…and this […]
The post Virginia Beer Co. Celebrates Harvest Season With Two Wet-Hopped Recipes appeared first on CraftBeer.com.
 Andreas Krennmair joins me this week to discuss his new book on the history of Vienna Lagers. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]
Andreas Krennmair joins me this week to discuss his new book on the history of Vienna Lagers. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics in […]  This week Marshall Schott joins me to discuss how many “short and shoddy” shortcuts you can take when brewing beer and still produce good beer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser […]
This week Marshall Schott joins me to discuss how many “short and shoddy” shortcuts you can take when brewing beer and still produce good beer. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser […]  Gary Glass joins me this week to discuss the state of US Craft and Homebrewing, the upcoming virtual Homebrewcon and some of his own homebrew creations. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your […]
Gary Glass joins me this week to discuss the state of US Craft and Homebrewing, the upcoming virtual Homebrewcon and some of his own homebrew creations. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your […]  Steve Piatz, the author of “The Complete Guide to Making Mead” joins me this week to discuss mead making techniques. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio […]
Steve Piatz, the author of “The Complete Guide to Making Mead” joins me this week to discuss mead making techniques. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or Spotify or Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio […] 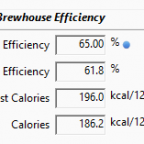 This week I take a look at how you can use BeerSmith brewing software to adjust the brewhouse efficiency for your individual equipment setup. Understanding Brewhouse Efficiency Brewhouse efficiency is simply a measure of how efficient your all grain brewing system is at converting pounds (or kilograms) of grains into Original Gravity (OG) points going […]
This week I take a look at how you can use BeerSmith brewing software to adjust the brewhouse efficiency for your individual equipment setup. Understanding Brewhouse Efficiency Brewhouse efficiency is simply a measure of how efficient your all grain brewing system is at converting pounds (or kilograms) of grains into Original Gravity (OG) points going […]  Ted Fleming joins me this week from Partake Brewing to discuss how to brew alcohol free beer at home. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or on Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […]
Ted Fleming joins me this week from Partake Brewing to discuss how to brew alcohol free beer at home. Subscribe on iTunes to Audio version or Video version or on Google Play Download the MP3 File– Right Click and Save As to download this mp3 file. Your browser does not support the audio element. Topics […] 


